7778-80-5
- Product Name:Potassium sulfate(VI)
- Molecular Formula:K2SO4
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:174.26
Product Details;
CasNo: 7778-80-5
Molecular Formula: K2SO4
Appearance: White crystalline solid
Cosmetics Grade Potassium sulfate(VI) 7778-80-5 For Sale with Good Price
- Molecular Formula:K2SO4
- Molecular Weight:174.26
- Appearance/Colour:White crystalline solid
- Melting Point:1069 °C, 1342 K, 1956 °F
- Boiling Point:1689 °C, 1962 K, 3072 °F
- Flash Point:1689°C
- PSA:88.64000
- Density:2.332 g/cm3
- LogP:-0.25720
Potassium sulfate(VI)(Cas 7778-80-5) Usage
|
Importance in Agriculture |
Potassium sulfate is a crucial fertilizer in agriculture. It contains potassium and sulfur, essential elements for crop growth and development.Potassium promotes photosynthesis, while sulfur enhances crop quality. |
|
Other Uses |
Glass industry: Used as a precipitant. |
|
Production Methods |
Extraction from Sea and Lake Salt Brine: |
|
General Description |
Potassium sulfate (VI), also known as dipotassium sulfate, is a chemical compound with the formula K2SO4. It is a colorless or white crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water. Potassium sulfate is commonly used as a fertilizer because of its high potassium content, which is essential for plant growth and development. It is also used in the manufacturing of glass, ceramics, and cement, as well as in the synthesis of other chemicals. In addition, potassium sulfate has a variety of industrial applications, including in the production of potassium alum and as a component in fire extinguishing powders. Overall, potassium sulfate is a versatile compound with numerous uses in agriculture, industry, and everyday products. |
InChI:InChI=1/2K.H2O4S/c;;1-5(2,3)4/h;;(H2,1,2,3,4)/q2*+1;/p-2
Relevant Products
-
PEG MGF
CAS:12020-86-9
-
114977-28-5
CAS:114977-28-5
-
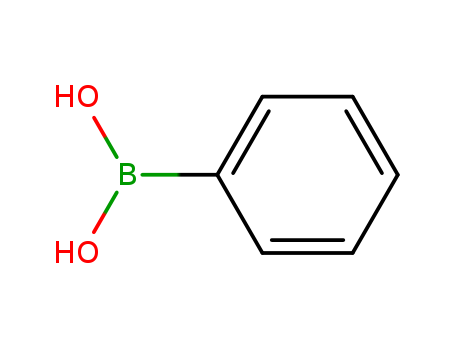
Phenylboronic acid
CAS:98-80-6