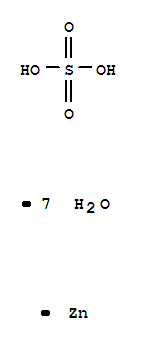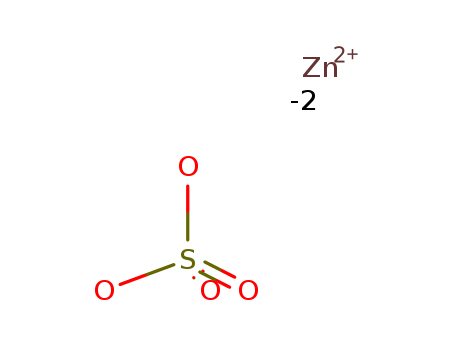
7733-02-0
- Product Name:Zinc sulphate
- Molecular Formula:ZnSO4
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:161.454
Product Details;
CasNo: 7733-02-0
Molecular Formula: ZnSO4
Appearance: colorless solid
Manufacturer supply high quality Zinc sulphate 7733-02-0 with ISO standards
- Molecular Formula:ZnSO4
- Molecular Weight:161.454
- Appearance/Colour:colorless solid
- Melting Point:100 °C
- Boiling Point:330 °C at 760 mmHg
- PSA:82.98000
- Density:1.31 g/mL at 20 °C
- LogP:0.42550
Zinc sulphate(Cas 7733-02-0) Usage
|
Indications |
Convergence preservatives: as eye drops, can be used for the treatment of conjunctivitis, trachoma, nasal blepharitis and so on. Oral stimulation of gastric mucosa can cause reflex vomiting. It can be used as emetic drug, now less used. It can be used for the treatment of zinc deficiency: zinc is the ingredient of many important enzymes in vivo such as carbonic anhydrase and alkaline phosphatase, being an indispensable trace element in the human body. Supplementation of zinc can be used for treating zinc deficiency such as dwarfism, acral dermatitis and zinc deficiency caused by long-term vein nutritional deficiency and so on. It can be used for the treatment of zinc deficiency related diseases: such as acne vulgaris, skin ulcers (venous, arterial, leprosy), psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, chronic eczema, oral ulcers, hair loss and smell taste disorders. It can be used as mordant for printing and dyeing, wood preservative, bleaching agent for papermaking, also used in medicine, artificial fiber, electrolysis, electroplating, and pesticide as well as zinc salt production. |
|
Production Methods |
Zinc sulfate is produced as an intermediate in recovering zinc from mineral zinc blende, ZnS (see Zinc, Recovery). The mineral is roasted at about 1,000°C to form zinc oxide and sulfur dioxide which, on prolonged heating in excess air, converts to zinc sulfate: 2ZnS + 3O2 → 2ZnO + 2SO2 992 ZINC SULFATE2ZnO + 2SO2 + O2 → 2ZnSO4 In the zinc recovery process, roasted products are leached with sulfuric acid, whereupon zinc oxide is converted to sulfate. ZnO + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2O Also, zinc sulfate can be prepared by reacting metallic zinc with dilute sulfuric acid followed by evaporation and crystallization: Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2 |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Water soluble. Efflorescent in air. Aqueous solutions are acidic. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Acidic salts, such as Zinc sulphate, are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydrogen ions and have pH's of less than 7.0. They react as acids to neutralize bases. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of inorganic acids, inorganic oxoacids, and carboxylic acid. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible. Many of these compounds catalyze organic reactions. |
|
Health Hazard |
Inhalation of dust causes irritation of nose and throat. Ingestion can cause irritation or corrosion of the alimentary tract. Contact with eyes or skin causes irritation. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Zinc sulfate?solution is as potent as formalin. This chemical is mainly used to treat footrot. It may also be used to treat acute bronchiolitis. |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, and intravenous routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: acute pulmonary edema, agranulocytosis, blood pressure decrease, diarrhea and other gastrointestinal changes, hypermotility, increased pulse rate without blood pressure decrease, level changes for metals other than Na/K/Fe/Ca/P/Cl, microcytosis with or without anemia, normocytic anemia. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Human mutation data reported. An eye irritant. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of SOx and ZnO. See also SULFATES and ZINC COMPOUNDS. |
|
Role in Flotation Processes |
Zinc sulfate (ZnSO4) is utilized as an inorganic depressant in flotation processes, particularly in the selective flotation of minerals. It is commonly used to depress sphalerite, a mineral often associated with other metal-sulfide minerals. Zinc sulfate depresses sphalerite before the flotation of other sulfide minerals to maximize the recovery of valuable resources. |
|
Activation of Depressed Sphalerite |
In flotation processing, the activation of depressed sphalerite is necessary for the maximum recovery of zinc resources. Lead nitrate (Pb(NO3)2) is used to activate the depressed sphalerite surface treated with zinc sulfate (ZnSO4). This activation step facilitates the flotation of sphalerite and enhances resource recovery. |
|
Biofortification of Banana Fruit |
Zinc sulfate is used for the biofortification of banana fruit through injections into the pseudostem of banana trees. This method involves injecting solutions containing zinc sulfate directly into the plant's vascular system (xylem), which facilitates the uptake of zinc by the banana plant. As a result, zinc is transported to the fruits, enhancing their nutritional value. |
|
Immunostimulant for Viral Diseases |
Zinc sulfate is proposed as a novel vaccine immunostimulant for challenging viral diseases like African swine fever (ASF) or COVID-19. This suggests that zinc sulfate may have immunostimulatory properties that could potentially enhance the efficacy of vaccines against these diseases. |
|
Physical properties |
The anhydrous sulfate is a colorless rhombohedral crystalline solid; refractive index 1.658; density 3.54 g/cm3; decomposes at 600°C; soluble in water, methanol, and glycerol.The heptahydrate, ZnSO4?7H2O, is a colorless crystalline solid; metallic taste; rhombohedral crystals; effloresces; refractive index 1.457; density 1.957 g/cm3 at 25°C; melts at 100°C; loses all its water molecules at 280°C; decomposes above 500°C; very soluble in water, 96.5 g/100mL at 20°C; soluble in glycerol, 40 g/100 mL; insoluble in alcohol The hexahydrate, ZnSO4?6H2O constitutes colorless monoclinic or tetragonal crystals; density 2.072 g/cm3at 15°C; loses five water molecules at 70°C; soluble in water. |
|
Definition |
zinc sulphate: A white crystalline water-soluble compound made by heating zinc sulphide ore in air and dissolving out and recrystallizing the sulphate. The common form is the heptahydrate, ZnSO4.7H2O; r.d. 1.9. This loses water above 30°C to give the hexahydrate and more water is lost above 70°C to form the monohydrate. The anhydrous salt forms at 280°C and this decomposes above 500°C. The compound, which was formerly called white vitriol, is used as a mordant and as a styptic (to check bleeding). |
|
General Description |
Anhydrous Zinc sulphate is a colorless crystalline solid. Zinc sulphate is also obtained as a hexahydrate, ZnSO4.6H2O, and as a heptahydrate ZnSO4.7H2O. All forms are soluble in water. All are noncombustible. The primary hazard is the threat posed to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Zinc sulphate is used in the production of rayon, as a feed supplement, used to obtaine lectrolyte zinc, in printing textiles and to make lithopone, to impregnate wood and hides,as an additive to spinning baths for production of synthetic silks, in electroplating, and in animal feeds. |
|
Agricultural Uses |
White vitriol is another name for zinc sulphate heptahydrate, and is a commonly used zinc salt. It is widely used as a fertilizer for overcoming zinc deficiency. |
|
Industrial uses |
Ferro sulfate (FeSO4·7H2O) is a crystalline substance greenish in color, with a specific gravity of 1.899. Ferro sulfate is obtained from various solutions using a vacuum crystallization method. Ferro sulfate has been used as a depressant and co-depressant in the following applications: (a) depression of sphalerite together with cyanide , (b) depression of fine molybdenite also with cyanide, and (c) in copper/lead separation using a method, based on copper depression by cyanide. |
InChI:InChI=1/H2O4S.Zn/c1-5(2,3)4;/h(H2,1,2,3,4);/p-2
7733-02-0 Relevant articles
Stability and reactivity of coordination and inclusion compounds in the reversible processes of thermal dissociation
Logvinenko
, p. 293 - 299 (1999)
The thermoanalytical approach to the stu...
Effusion Studies of the Decomposition of Zinc Sulfate and Zinc Oxysulfate
Brittain, R. D.,Lau, K. H.,Knittel, D. R.,Hildenbrand, D. L.
, p. 2259 - 2264 (1986)
The torsion-effusion method has been use...
Crystallization and characterization of the compounds Gly·MSO 4·mH2O (M = Mg2+, Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Zn2+; M = 0, 3, 5, 6)
Tepavitcharova,Rabadjieva,Havlí?ek,Němec,Vojtí?ek,Plocek,Koleva
, p. 113 - 121 (2012)
The equilibrium crystallization of compl...
Spectral and thermal studies on new hydrazinium metal sulfite dihydrates
Vikram,Shanthakumar,Ragul,Sivasankar
, p. 521 - 524 (2007)
Some new hydrazinium transition metal su...
Oxidation of a ZnS nanobelt into a ZnO nanotwin belt or double single-crystalline ZnO nanobelts
Li, Yujie,You, Liping,Duan, Ran,Shi, Pengbo,Qin, Guogang
, p. 233 - 238 (2004)
Single-crystalline wurtzite ZnS nanobelt...
AQUEOUS COMPOSITION AND METHOD OF PRODUCING CHLORINE DIOXIDE USING AQUEOUS COMPOSITION
-
, (2018/07/15)
An aqueous composition includes an activ...
Interpenetrated and Catenated Zinc Thiosulfates Frameworks with dia and qtz Nets: Synthesis, Structure, and Properties
Karthik, Rajendran,Natarajan, Srinivasan
, p. 2239 - 2248 (2016/05/09)
Reactions between Zn(NO3)2·6H2O, Na2S2O3...
METHOD OF PROMOTING WOUND HEALING
-
Page/Page column, (2015/03/16)
A method of establishing a therapeutic w...
7733-02-0 Process route
-
-
(Zn0218Al0.612(OH)2)(S(01)O4)36*0.6H2O

-
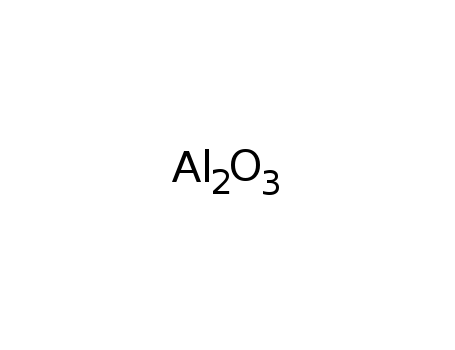
-
1333-84-2,1344-28-1
aluminum oxide
-
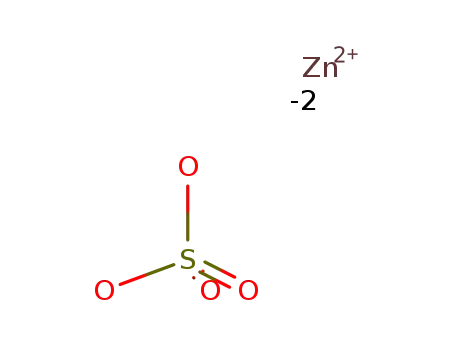
-
7733-02-0
zinc(II) sulfate

-

-
zinc(II) oxide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In
neat (no solvent);
byproducts: H2); heated in flowing air at 200-600°C; detd. by thermogravimetric analysis;
|
-
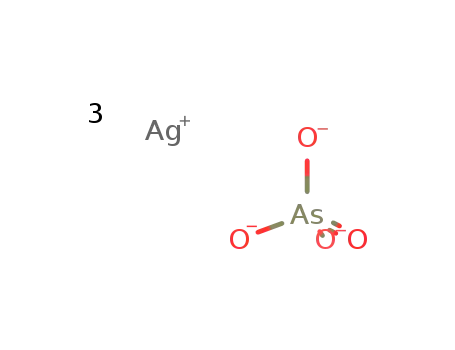
-
trisilver arsenate

-

-
7440-66-6
zinc

-
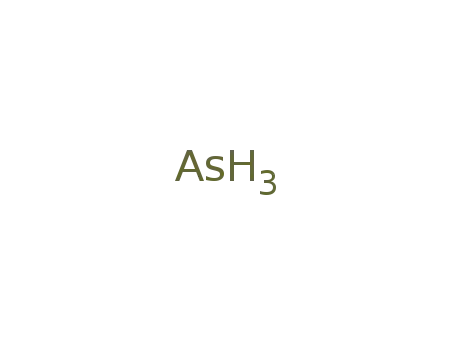
-
7440-38-2,460345-38-4,7784-42-1,127323-69-7
arsenic

-
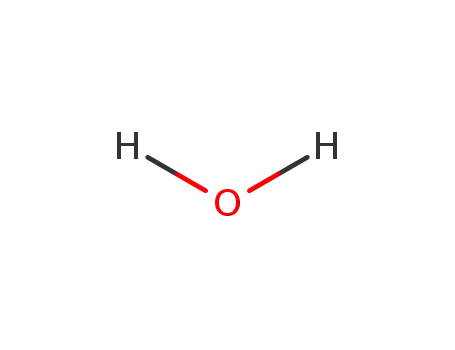
-
7732-18-5
water

-

-
7440-22-4
silver

-

-
7733-02-0
zinc(II) sulfate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
sulfuric acid;
In
sulfuric acid;
|
|
|
With
H2SO4;
In
sulfuric acid;
|
7733-02-0 Upstream products
-
743369-26-8
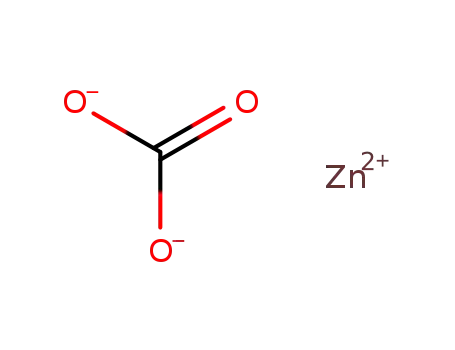
zinc(II) carbonate
-
77-78-1
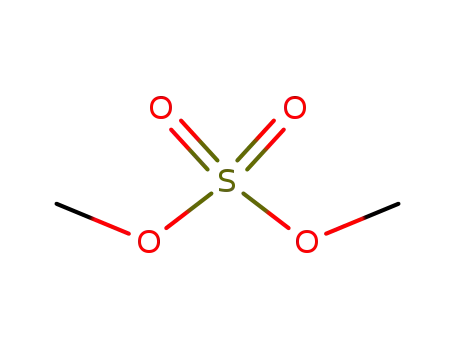
dimethyl sulfate
-
7732-18-5

water
-
10028-15-6
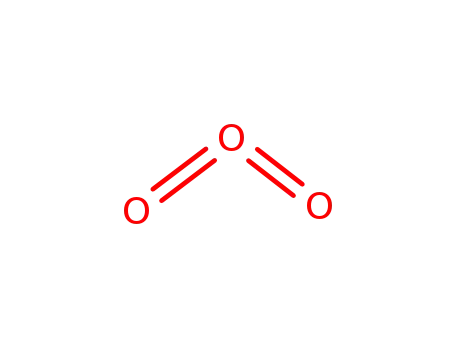
ozone
7733-02-0 Downstream products
-
10028-15-6

ozone
-
7446-11-9
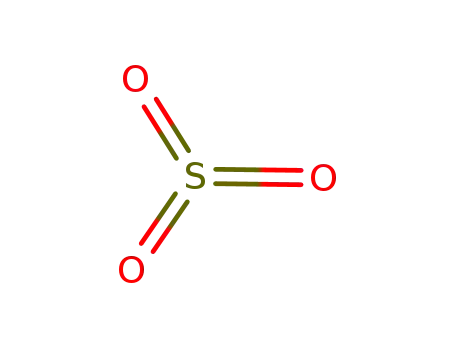
sulfur trioxide
-
7440-66-6

zinc
-
7446-09-5
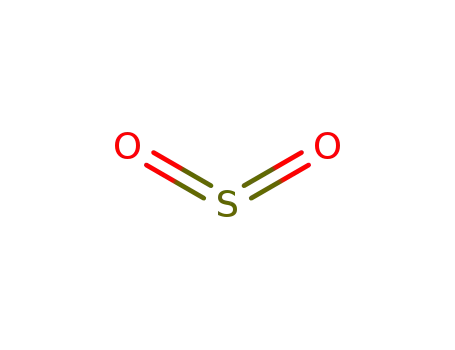
sulfur dioxide
Relevant Products
-
Zinc sulfate heptahydrate
CAS:7446-20-0
-
Matrine
CAS:519-02-8
-
L(+)-Citrulline
CAS:372-75-8