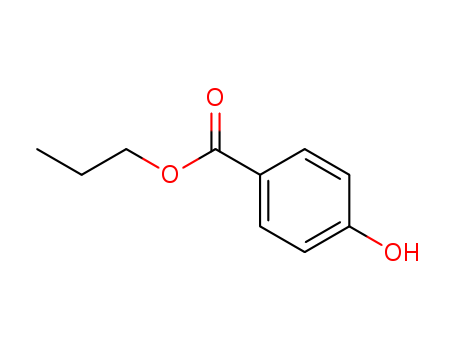
94-13-3
- Product Name:Propylparaben
- Molecular Formula:C10H12O3
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:180.203
Product Details;
CasNo: 94-13-3
Molecular Formula: C10H12O3
Appearance: white crystalline powder
Factory supply Propylparaben 94-13-3 with sufficient stock and high standard
- Molecular Formula:C10H12O3
- Molecular Weight:180.203
- Appearance/Colour:white crystalline powder
- Vapor Pressure:0.00093mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:95-98 °C(lit.)
- Refractive Index:1.5050
- Boiling Point:294.3 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:pKa 8.4 (Uncertain)
- Flash Point:124.6 °C
- PSA:46.53000
- Density:1.134 g/cm3
- LogP:1.95900
Propylparaben(Cas 94-13-3) Usage
|
content analysis |
Same with Method 1 in "Butyl p-hydroxybenzoate (07002)". In calculation, per mL of 1 mol/L sodium hydroxide corresponds to 180.2mg of this goods (C10Hl2O8). |
|
Toxicity |
Adl? 0-10 mg/kg (FAO/WHO, 2001). LD50? 3.7g/kg (mouse, oral). GRAS? (FDA, § 184.1670, 2000). HACSG? listed in the restricted list. |
|
usage limits |
2760--2002 GB (calculate in p-hydroxybenzoic acid; g/kg): fresh fruit and vegetable 0.012; vinegar 0.10; carbonated beverages 0.20; fruit juice (fruit flavor) type beverages, jam (excluding canned), soy sauces 0.25; pastry stuffing 0.5 (the total amount of single use or mixed use with ethyl 4-hydroxybenzoate); egg yolk filling 0.20. Another provision that sodium methylparaben is also equivalent application. FAO/WHO (1984): Jam and jelly, 1000 mg/kg FDA § 184.1670 (2000): 0.1%. EEC(1990, mg/kg): Frozen drinks 160; beet pickled vegetables, salad dressings, 250; fragrance, fruit tarts, purees, concentrated soft drinks, 800; Fruit canned, salted fish, 1000. Japan (calculate in p-hydroxybenzoic acid, g/kg; this product, g): soy sauce 0.25g/L (this product 0.32); vinegarsoysoy 0.1g/L (This product 0.13); soft drinks and syrup 0.1 (this product 0.13); fruit sauce 0.2 (this product 0.26); fruits and vegetables 0.012 (this product 0.015). |
|
Production methods |
This product can be derived from the esterification of p-hydroxybenzoic acid and n-propanol. First mix p-hydroxybenzoic acid with propanol and heat to dissolve. Then add sulfuric acid slowly and continue to heat for 8h of refluxion. After cooling, pour them into the 4% sodium carbonate solution for precipitation and crystallization. Filtrate and wash to neutral to obtain the crude product. After further ethanol recrystallization, the finished products are obtained. In the preparation, the cation exchange resin can be used in place of the sulfuric acid catalyst. It can be derived from the esterification of p-hydroxybenzoic acid and n-propanol in the presence of sulfuric acid. Add p-hydroxybenzoic acid and n-propanol in turn to the esterification reactor, and heat to dissolve. Add concentrated sulfuric acid slowly and heat for 8h of refluxion. Pour the reaction solution into 4% sodium carbonate solution before it is cooled. Constantly stir for precipitation and crystallization. Then the crude product can be obtained after centrifugal filtration and washed to neutral. Finally the finished product is acquired after activated carbon decolorization and ethanol recrystallization. The method of preparing ethyl p-hydroxybenzoate can also be used as a reference. HOC6H4COOH + C3H7OH [H2SO4] → HOC6H4COOC3H7 + H2O |
|
Hazards & Safety Information |
Category: Toxic substances Toxicity classification :Moderate toxicity Acute Toxicity :Celiac-mouse LD50: 200 mg/kg Flammable hazardous characteristics :Flammable; excrete acrid and pungent smoke from fire Storage and transport characteristics :Stored in the low-temperature, well-ventilated and dry warehouse Fire extinguishing agent :water, carbon dioxide, dry powder, sand |
|
Production Methods |
Propylparaben is prepared by the esterification of p-hydroxybenzoic acid with n-propanol. |
|
Preparation |
Produced by esterfying p-hydroxybenzoic acid with n-propanol, using an acid catalyst such as sulfuric acid and an excess of propanol. The materials are heated in a glass-lined reactor under reflux. The acid is then neutralized with caustic soda and the product is crystallized by cooling. The crystallized product is centrifuged, washed, dried under vacuum, milled and blended, all in corrosion-resistant equipment to avoid metallic contamination. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Maximum stability of Propylparaben occurs at a pH of 4 to 5. Incompatible with alkalis and iron salts. Also incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and strong acids . |
|
Fire Hazard |
Flash point data for Propylparaben are not available; however, Propylparaben is probably combustible. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Nonflammable |
|
Pharmaceutical Applications |
Propylparaben is widely used as an antimicrobial preservative in cosmetics, food products, and pharmaceutical formulations. It may be used alone, in combination with other paraben esters, or with other antimicrobial agents. It is one of the most frequently used preservatives in cosmetics. The parabens are effective over a wide pH range and have a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity, although they are most effective against yeasts and molds. Owing to the poor solubility of the parabens, the paraben salts, particularly the sodium salt, are frequently used in formulations. This may cause the pH of poorly buffered formulations to become more alkaline. Propylparaben (0.02% w/v) together with methylparaben (0.18% w/v) has been used for the preservation of various parenteral pharmaceutical formulations. |
|
Contact allergens |
This substance is one of the parabens family. Parabens are esters formed by p-hydroxybenzoic acid and an alcohol. They are largely used as biocides in cosmetics and toiletries, medicaments, or food. They have synergistic power with other biocides. Parabens can induce allergic contact dermatitis, mainly in chronic dermatitis and wounded skin. |
|
Safety |
Propylparaben and other parabens are widely used as antimicrobial preservatives in cosmetics, food products, and oral and topical pharmaceutical formulations. Propylparaben and methylparaben have been used as preservatives in injections and ophthalmic preparations; however, they are now generally regarded as being unsuitable for these types of formulations owing to the irritant potential of the parabens. Systemically, no adverse reactions to parabens have been reported, although they have been associated with hypersensitivity reactions. The WHO has set an estimated acceptable total daily intake for methyl, ethyl, and propyl parabens at up to 10 mg/kg body-weight. LD50 (mouse, IP): 0.2 g/kg LD50 (mouse, oral): 6.33 g/kg LD50 (mouse, SC): 1.65 g/kg |
|
storage |
Aqueous propylparaben solutions at pH 3–6 can be sterilized by autoclaving, without decomposition.At pH 3–6, aqueous solutions are stable (less than 10% decomposition) for up to about 4 years at room temperature, while solutions at pH 8 or above are subject to rapid hydrolysis (10% or more after about 60 days at room temperature). |
|
Incompatibilities |
The antimicrobial activity of propylparaben is reduced considerably in the presence of nonionic surfactants as a result of micellization. Absorption of propylparaben by plastics has been reported, with the amount absorbed dependent upon the type of plastic and the vehicle. Magnesium aluminum silicate, magnesium trisilicate, yellow iron oxide, and ultramarine blue have also been reported to absorb propylparaben, thereby reducing preservative efficacy. Propylparaben is discolored in the presence of iron and is subject to hydrolysis by weak alkalis and strong acids. |
|
Regulatory Status |
Propylparaben and methylparaben are affirmed GRAS direct food substances in the USA at levels up to 0.1%. All esters except the benzyl ester are allowed for injection in Japan. In cosmetics, the EU and Brazil allow use of each paraben at 0.4%, but the total of all parabens may not exceed 0.8%. The upper limit in Japan is 1.0%. Accepted as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (IM, IV, and SC injections; inhalations; ophthalmic preparations; oral capsules, solutions, suspensions, and tablets; otic, rectal, topical, and vaginal preparations). Included in parenteral and nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients. |
|
Chemical Composition and Structure |
Propylparaben is an ester of p-hydroxybenzoic acid (PHBA), specifically the propyl ester.[1] |
|
Chemical properties |
Propylparaben is a colorless and fine crystalline or white crystalline powder, almost odorless and with slightly astringent.Soluble in ethanol, ethyl ether, acetone and other organic solvents, slightly soluble in water. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: The benzoate ester that is the propyl ester of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid. Preservative typically found in many water-based cosmetics, such as creams, lotions, shampoos and bath products. Also used as a food additive. |
|
General Description |
Colorless crystals or white powder or chunky white solid. Melting point 95-98°C. Odorless or faint aromatic odor. Low toxicity, Tasteless (numbs the tongue). pH: 6.5-7.0 (slightly acidic) in solution. |
InChI:InChI=1/C10H12O3/c1-2-7-13-10(12)8-3-5-9(11)6-4-8/h3-6,11H,2,7H2,1H3
94-13-3 Relevant articles
Method for preparing paraben
-
Paragraph 0029-0032, (2020/03/25)
The invention discloses a method for pre...
Proline ionic liquid and method for catalyzing synthesis of paraben by proline ionic liquid
-
Paragraph 0051-0054, (2020/09/16)
The invention discloses proline ionic li...
A process for preparing Nepal jin zhi method (by machine translation)
-
Paragraph 0042; 0043; 0044; 0045; 0046; 0047; 0048, (2019/10/02)
The invention discloses a method for pre...
Method for preparing parabens
-
Paragraph 0026; 0030-0032; 0048; 0050-0053, (2019/07/01)
The invention discloses a method for pre...
94-13-3 Process route
-
-
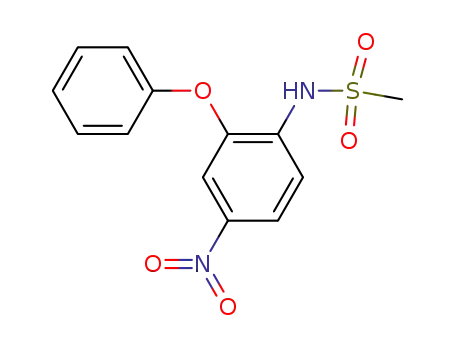
51803-78-2
nimesulide

-
-
94-13-3
nipasol
-
-
62-44-2,105931-34-8
4-ethoxyacetanilide

-
-
5422-92-4
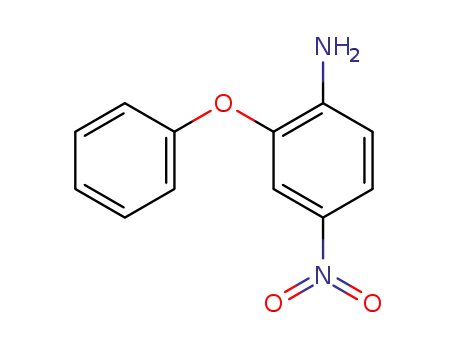
1-amino-2-phenoxy-4-nitrobenzene

-
-
99-76-3,156291-94-0
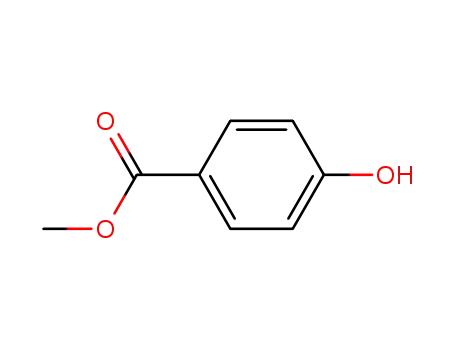
methyl 4-hydroxylbenzoate

-
-
99-96-7
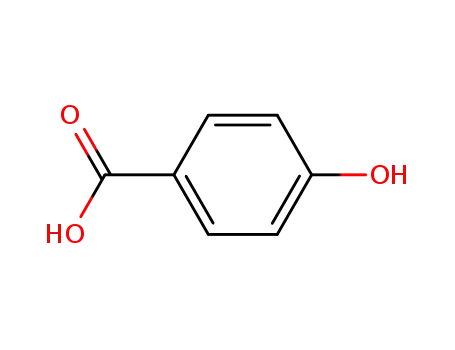
4-hydroxy-benzoic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
water; sodium hydroxide;
In
methanol;
at 90 ℃;
for 2h;
|
-
-
71-23-8
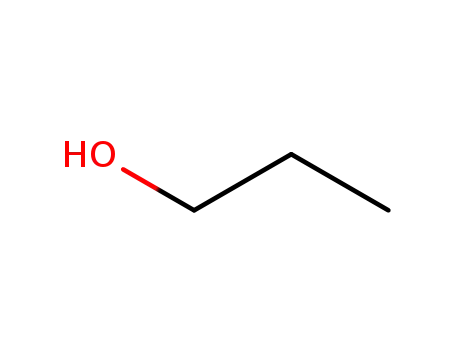
propan-1-ol

-

-
99-96-7
4-hydroxy-benzoic acid

-

-
94-13-3
nipasol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
methanesulfonic acid; choline chloride;
Reflux;
|
93.4% |
|
With
benzimidazole bisulfate ionic liquid;
Reflux;
|
93.8% |
|
With
NKC-9-type macroporous resin;
at 98 ℃;
for 3.08333h;
Temperature;
Microwave irradiation;
|
89% |
|
With
C11H14N2*C5H9NO2;
Reflux;
|
89% |
|
With
sodium hydroxide; sulfuric acid;
for 1h;
Heating;
|
79.5% |
|
With
vitriol;
at 97 ℃;
for 1h;
under 760 Torr;
microwave irradiation;
|
78% |
|
With
hydrogenchloride;
Erwaermen des mit Schwefelsaeure versetzten Reaktionsgemisches;
|
|
|
With
sulfuric acid;
|
|
|
With
hydrogenchloride;
|
|
|
With
sulfuric acid;
Heating;
|
|
|
With
sulfuric acid;
In
toluene;
for 0.0166667h;
Heating;
|
|
|
With
trifluoromethanesulfonic acid immobilized on zirconium oxide;
at 100 ℃;
for 5h;
Autoclave;
|
94-13-3 Upstream products
-
71-23-8

propan-1-ol
-
99-96-7

4-hydroxy-benzoic acid
-
27739-13-5
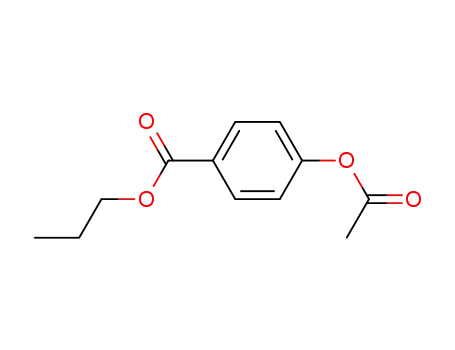
n-propyl 4-acetoxybenzoate
-
124-38-9
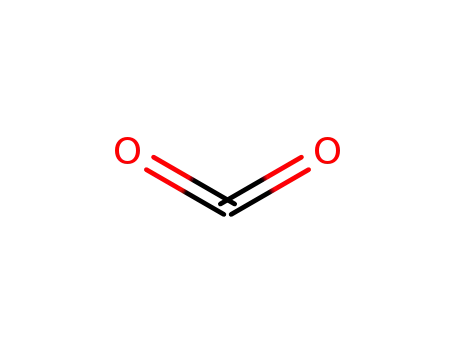
carbon dioxide
94-13-3 Downstream products
-
111222-67-4
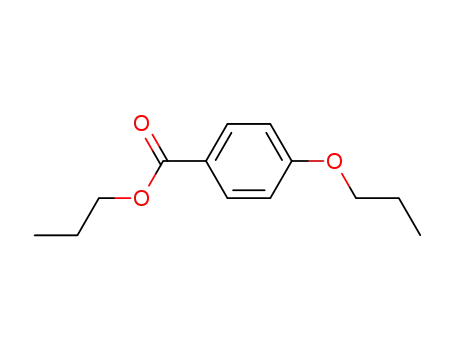
4-propoxy-benzoic acid propyl ester
-
69806-25-3
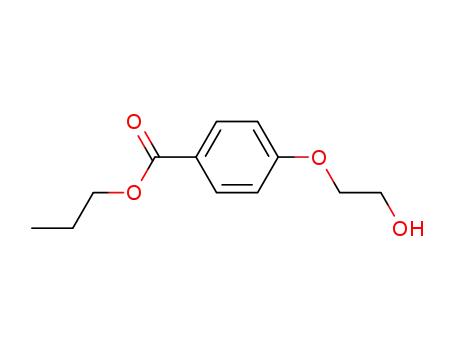
4-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-benzoic acid propyl ester
-
124103-78-2
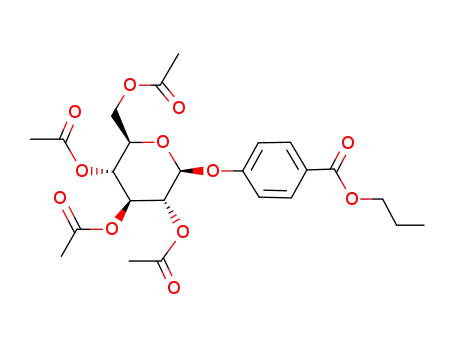
4-(Propoxycarbonyl)phenyl 2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranoside
-
56220-01-0
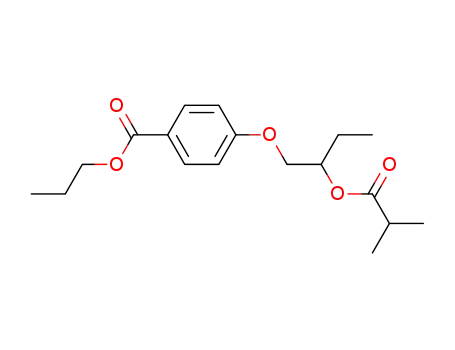
4-(2-Isobutyryloxy-butoxy)-benzoic acid propyl ester
Relevant Products
-
Tesamorelin
CAS:218949-48-5
-
PEG MGF
CAS:12020-86-9
-
Artemether
CAS:71963-77-4