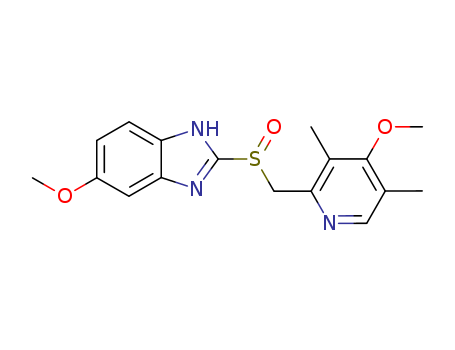
73590-58-6
- Product Name:Omeprazole
- Molecular Formula:C17H19N3O3S
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:345.422
Product Details;
CasNo: 73590-58-6
Molecular Formula: C17H19N3O3S
Appearance: white crystalline solid
Perfect Factory Offer Excellent quality Omeprazole 73590-58-6 with Safe Shipping
- Molecular Formula:C17H19N3O3S
- Molecular Weight:345.422
- Appearance/Colour:white crystalline solid
- Melting Point:156 °C
- Boiling Point:599.991 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:pKa 4.14/8.9(H2O,t =25,I=0.025) (Uncertain)
- Flash Point:316.663 °C
- PSA:96.31000
- Density:1.371 g/cm3
- LogP:3.76540
Omeprazole(Cas 73590-58-6) Usage
|
Preparation |
The antiulcer agent omeprazole is produced from 2,3,5-trimethylpyridine N-oxide.Synthesis and Structure of OmeprazoleSteps: 2-(Lithium methyl sulphinyl)-5-methoxy-1H benzimidazole 20g was reacted with 2-chloro-3,5-dimethyl-4-methoxy pyridine 21 g to form sulphide intermediate and then converted to Omeprazole when treated with m-CPBA which used as anoxidizingagents. The acetamide-sulfide compounds modification are oxidised to form the amide sulfinyl compound and gives the sulfinyl carboxylate or salts upon alkaline hydrolysis.On further decarboxylation leads to the target molecules. The residual, unreacted salt, inorganic by-products and other minor by-products can be easily purified by a simple washing from omeprazole or lansoprazole. The amide compounds containing crystalline solids as opposed to the sulphide and sulfoxides of the reported procedures.DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20902/IJPTR.2019.120307 |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Antiulcer |
|
World Health Organization (WHO) |
Omeprazole was introduced in the 1980s. It belongs to a group of agents that have an inhibitory effect on the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach (gastric acid proton pump inhibitors) and is used in the treatment of upper gastrointestinal tract disorders. The Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products of the European Commission has concluded that a causal association between the reactions reported in Germany and the use of omeprazole had not been established. Nevertheless oral administration should be preferred. (Reference: (CPMPPO) Pharmacovigilance Opinion, No.16 , , 25 July 1994) |
|
Biological Activity |
H + ,K + -ATPase inhibitor (IC 50 = 5.8 μ M) that displays antisecretory and antiulcer activity. Inhibits gastric acid secretion (IC 50 = 0.16 μ M for histamine-induced acid formation) and reduces gastric lesion formation induced by a variety of ulcerative stimuli. Antibacteral against Helicobacter pylori in vitro . Also inhibits CYP2C19, CYP2C9 and CYP3A (K i values are 3.1, 40.1 and 84.4 μ M respectively) and blocks swelling-dependent chloride channels (ICIswell). |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Omeprazole binds covalently to proton pump (H+, K+-ATPase) and inhibits gastric secretion. It is useful in ameliorating the effects of peptic oesophagitis, duodenal and gastric ulcer. Omeprazole is preferred over antagonists of histamine H2-receptor and ranitidine for its higher efficiency. It is also useful in treating Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. |
|
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments |
Omeprazole is potentially useful in treating both gastroduodenal ulcer disease and to prevent or treat gastric erosions caused by ulcerogenic drugs (e.g., aspirin). An oral paste product is labeled for the treatment and prevention of recurrence of gastric ulcers in horses. |
|
Drug interactions |
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Anticoagulants: effect of coumarins possibly enhanced. Antiepileptics: effects of phenytoin possibly enhanced. Antifungals: absorption of itraconazole and ketoconazole reduced; avoid with posaconazole; concentration increased by voriconazole. Antivirals: reduced atazanavir concentration - avoid; AUC of saquinavir increased by 82% (increased risk of toxicity) - avoid; concentration of raltegravir possibly increased - avoid; concentration of rilpivirine reduced - avoid; concentration of omeprazole reduced by tipranavir. Ciclosporin: variable response; mostly increase in ciclosporin level. Cilostazol: increased cilostazol concentration - reduce cilostazol dose. Clopidogrel: avoid due to reduced efficacy of clopidogrel. Cytotoxics: possibly reduced excretion of methotrexate; avoid with erlotinib and vandetanib; possibly reduced dasatinib and lapatinib absorption - avoid with dasatinib; possibly reduced absorption of pazopanib. Tacrolimus: may increase tacrolimus concentration. Ulipristal: reduced contraceptive effect, avoid with high dose ulipristal. |
|
Metabolic pathway |
When male humans are given 14C-omeprazole orally, an average of 79% of the dose is recovered in the urine in 96 h. Omeprazole is completely metabolized and at least six metabolites are identified. Two major metabolites are hydroxyomeprazole and omeprazole acid. |
|
Metabolism |
Omeprazole is completely metabolised in the liver by the cytochrome P450 system to form inactive metabolites which are excreted mostly in the urine and to a lesser extent in bile. CYP2C19 produces hydroxyomeprazole, the major metabolite, CYP3A4 produces omeprazole sulphone. |
|
Mode of action |
Omeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor which can specifically act on gastric parietal cell proton pump sites and transform into the active form of sulfonamide, then irreversibly binds to the proton pumps through disulfide bonds, generating a sulfonamide and proton pump compound (H + -K + -ATP), thereby inhibiting the enzymatic activity, preventing the H+ in parietal cells from being transported to the stomach cavity. It has a strong and persistent inhibitory role on gastric acid secretion caused by basal gastric acid and pentapeptide gastric acid secretions, greatly reducing gastric acid within the gastric juice. Rapid, reversible, and no H2 antagonist-induced psychiatric side effects. |
|
Mechanism of Action |
Omeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that inhibits the H+/K+ ATPase in gastric cells, reducing proton secretion into the gastric lumen. It also inhibits vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase), potentially exerting antiproliferative effects in tumor cells. |
|
Medical Uses |
Used to treat various gastrointestinal disorders such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), gastric ulcers, duodenal ulcers, upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract inflammatory conditions, eosinophilic esophagitis, and erosive esophagitis. Also employed in the treatment of hypersecretory conditions like Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Combined with antibiotics for eradicating Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). |
|
Pharmacokinetics |
Metabolized primarily by the CYP2C19 enzyme. Response to omeprazole can vary based on CYP2C19 metabolizer status, with rapid metabolizers potentially needing higher doses for efficacy and poor metabolizers requiring lower doses. Dosing recommendations vary among different metabolizer phenotypes, with ultrarapid metabolizers potentially needing increased doses for H. pylori eradication. |
|
Global Variation in Metabolizer Phenotypes |
Frequencies of CYP2C19 metabolizer phenotypes differ among global populations, with implications for dosing. |
|
Pharmacogenetics Recommendations |
Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) recommends dose adjustments for different metabolizer phenotypes. |
|
Superiority in Acid Inhibition |
Omeprazole is a potent inhibitor of gastric acid secretion, demonstrating superiority over previous treatments for GERD and peptic ulcers. It concentrates specifically in the acidic canalicular space of parietal cells where it inhibits the proton pump. |
|
Research on Antiproliferative Effects |
Omeprazole has shown inhibition of pancreatic cancer cell growth and promotion of apoptosis in human melanoma cells and B-cell malignancies. |
|
Application |
Omeprazole is a benzimidazole with selective and irreversible proton pump inhibition activity. Omeprazole forms a stable disulfide bond with the sulfhydryl group of the hydrogen-potassium (H+ - K+) ATPase found on the secretory surface of parietal cells, thereby inhibiting the final transport of hydrogen ions (via exchange with potassium ions) into the gastric lumen and suppressing gastric acid secretion. This agent exhibits no anticholinergic activities and does not antagonize histamine H2 receptors. Omeprazole Pellets are used in the treatment of Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): A condition in which backward flow of acid from the stomach causes heartburn and injury of the food pipe (esophagus). |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: Omeprazole is a member of the class of benzimidazoles that is 1H-benzimidazole which is substituted by a [4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methyl]sulfinyl group at position 2 and a methoxy group at position 5. |
|
Brand name |
Prilosec (Astra Zeneca). |
|
General Description |
Omeprazole, 5-methoxy-2-(((4-methoxy-3, 5-dimethyl-2-pyridinyl)methyl) sulfinyl)-1Hbenzimidazole(Losec), is a white to off-white crystallinepowder with very slight solubility in water. Omeprazole isan amphoteric compound (pyridine N, pKa 4.06; benzimidazoleN-H, pKa 0.79), and consistent with the proposedmechanism of action of the substituted benzimidazoles, isacid labile. Hence, the omeprazole product is formulatedas delayed-release capsules containing enteric-coatedgranules.The absolute bioavailability of orally administeredorneprazole is 30% to 40% related to substantial first-passbiotransformation. The drug has a plasmahalf-life of about 1 hour. Most (77%) of an oral dose ofomeprazole is excreted in the urine as metabolites with insignificantantisecretory activity. The primary metabolitesof omeprazole are 5-hydroxyomeprazole (CYP2C19) andomeprazole sulfone (CYP3A4). The antisecretory actions ofomeprazole persist for 24 to 72 hours, long after the drughas disappeared from plasma, which is consistent with itssuggested mechanism of action involving irreversible inhibitionof the proton pump.Omeprazole is approved for the treatment of heartburn,GERD, duodenal ulcer, erosive esophagitis, gastric ulcer,and pathological hypersecretory conditions. |
InChI:InChI=1/C17H19N3O3S/c1-10-8-18-15(11(2)16(10)23-4)9-24(21)17-19-13-6-5-12(22-3)7-14(13)20-17/h5-8H,9H2,1-4H3,(H,19,20)
73590-58-6 Relevant articles
Monitoring and Quantification of Omeprazole Synthesis Reaction by In-Line Raman Spectroscopy and Characterization of the Reaction Components
?ahni?, Damir,Me?trovi?, Ernest,Jedna?ak, Tomislav,Habinovec, Iva,Parlov Vukovi?, Jelena,Novak, Predrag
, p. 2092 - 2099 (2016)
The development of a quantitative in-lin...
A mild and chemoselective CALB biocatalysed synthesis of sulfoxides exploiting the dual role of AcOEt as solvent and reagent
Anselmi, Silvia,Liu, Siyu,Kim, Seong-Heun,Barry, Sarah M.,Moody, Thomas S.,Castagnolo, Daniele
supporting information, p. 156 - 161 (2021/01/14)
A mild, chemoselective and sustainable b...
Selective synthesis of sulfoxides and sulfonesviacontrollable oxidation of sulfides withN-fluorobenzenesulfonimide
Cao, Zhong-Yan,Li, Xiaolong,Lu, Hao,Wang, Panpan,Wang, Shengqiang,Xu, Xiaobo,Yan, Leyu,Yang, A-Xiu
supporting information, p. 8691 - 8695 (2021/10/22)
A practical and mild method for the swit...
Preparation method of omeprazole and omeprazole
-
Paragraph 0049-0084, (2021/04/21)
The invention is applicable to the techn...
Synthesis method of esomeprazole sodium
-
Paragraph 0030; 0037-0039, (2021/10/20)
The invention discloses a synthesis meth...
73590-58-6 Process route
-
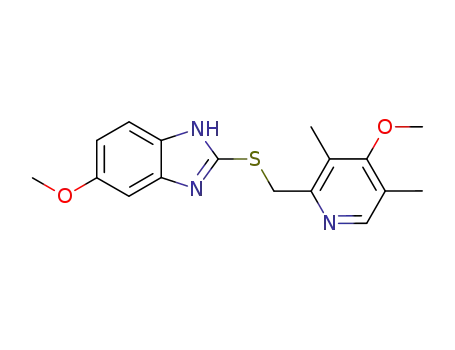
-
73590-85-9
omeprazole sulfide

-
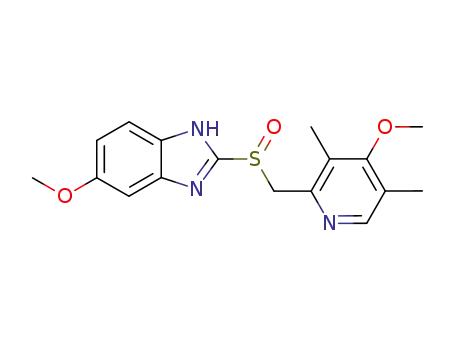
-
73590-58-6
omeprazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
dihydrogen peroxide;
molybdenyl acetylacetonate;
In
methanol; water;
at 0 - 5 ℃;
for 3h;
|
91% |
|
With
dihydrogen peroxide; sodium carbonate;
sodium tungstate;
In
methanol; water;
at 20 ℃;
for 0.666667h;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
91% |
|
With
sodium hydroxide; dihydrogen peroxide;
sodium tungstate;
In
methanol; water;
at 20 ℃;
for 0.666667h;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
88% |
|
omeprazole sulfide;
With
titanium(IV) isopropylate;
In
toluene;
at 30 ℃;
With
Cumene hydroperoxide;
In
toluene;
at 25 ℃;
for 5h;
Solvent;
Temperature;
Reagent/catalyst;
|
88% |
|
With
phthaloyl peroxide;
In
methanol;
at 25 ℃;
for 8h;
chemoselective reaction;
Schlenk technique;
|
88% |
|
omeprazole sulfide;
With
triethylamine;
In
ethanol;
at 40 ℃;
for 0.166667h;
pH=8-9;
With
dihydrogen peroxide;
In
ethanol;
for 3h;
Reagent/catalyst;
Temperature;
|
88.4% |
|
With
tert.-butylhydroperoxide;
bis(acetylacetonate)oxovanadium;
In
water; isopropyl alcohol;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
83.5% |
|
With
m-chloroperoxybenzoic acid;
In
ethyl acetate;
|
79.1% |
|
With
m-chloroperoxybenzoic acid; sodium carbonate;
In
ethyl acetate;
|
76.2% |
|
With
ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate; dihydrogen peroxide; sodium hydroxide;
In
methanol; water;
at 20 - 25 ℃;
for 1.58333h;
pH=9.3;
|
76.6% |
|
With
titanium(IV) isopropylate; D-tartaric acid; Cumene hydroperoxide; N-ethyl-N,N-diisopropylamine;
In
toluene;
at 20 - 65 ℃;
for 1h;
|
75% |
|
With
tert.-butylhydroperoxide;
bis(acetylacetonate)oxovanadium;
In
water; toluene;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
74.6% |
|
With
immobilised lipase B from Candida antarctica; urea hydrogen peroxide adduct; ethyl acetate;
In
dichloromethane;
at 37 ℃;
for 2h;
chemoselective reaction;
Enzymatic reaction;
|
73% |
|
With
dihydrogen peroxide;
sodium tungstate;
In
ethanol; water;
at 20 ℃;
for 6.5h;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
69% |
|
With
tert.-butylhydroperoxide;
bis(acetylacetonate)oxovanadium;
In
toluene;
at 5 - 22 ℃;
for 3h;
|
68.5% |
|
With
tert.-butylhydroperoxide;
bis(acetylacetonate)oxovanadium;
In
ethanol; water;
at 16 - 17 ℃;
for 3.08333h;
|
63% |
|
With
tert.-butylhydroperoxide;
bis(acetylacetonate)oxovanadium;
In
ethanol; water;
at 16 - 17 ℃;
for 3.08333h;
|
63% |
|
With
tert.-butylhydroperoxide;
vanadium(V) oxide;
In
ethanol; water;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
50% |
|
With
tert.-butylhydroperoxide;
sodium vanadate;
In
ethanol; water;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
50% |
|
With
tert.-butylhydroperoxide;
bis(acetylacetonate)oxovanadium;
In
methanol; water;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
50% |
|
With
oxone; sodium hydrogencarbonate;
In
ethanol; tetrabutylammomium bromide; water;
at 0 - 5 ℃;
for 2h;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
50.7% |
|
With
water; N-fluorobis(benzenesulfon)imide;
at 20 ℃;
for 24h;
chemoselective reaction;
|
46% |
|
With
dihydrogen peroxide;
bis(acetylacetonate)oxovanadium;
In
ethanol; water;
at 20 ℃;
for 12h;
|
32% |
|
With
dihydrogen peroxide;
bis(acetylacetonate)oxovanadium;
In
ethanol; water;
at 20 ℃;
for 12h;
|
32% |
|
With
sodium hydroxide; sodium hypochlorite;
In
dichloromethane; water;
at -5 - 0 ℃;
for 3h;
|
|
|
With
peracetic acid;
In
ethyl acetate;
|
|
|
With
3-chloro-benzenecarboperoxoic acid;
In
dichloromethane;
at 0 - 5 ℃;
for 0.333333 - 0.416667h;
|
|
|
With
trans-stilbene ozonide;
In
methanol;
for 3.5h;
Product distribution / selectivity;
Heating / reflux;
|
|
|
With
1-hexen-ozonide;
In
methanol;
for 3.5h;
Product distribution / selectivity;
Heating / reflux;
|
|
|
|
|
|
With
dihydrogen peroxide;
sodium molybdate;
In
water; acetic acid; ethyl acetate;
at 5 - 12 ℃;
for 6.75h;
pH=6 - 6.5;
|
|
|
With
dihydrogen peroxide;
bis(acetylacetonate)oxovanadium;
In
water; acetone;
at 10 - 15 ℃;
for 3.5h;
|
|
|
omeprazole sulfide;
With
diethyl (2S,3S)-tartrate; titanium propoxide;
In
water; toluene;
at 80 ℃;
for 1h;
With
Cumene hydroperoxide; N-ethyl-N,N-diisopropylamine;
In
water; toluene;
at 30 ℃;
for 1.5h;
|
|
|
With
ammonium dihydrogen phosphate; ammonium molybdate; dihydrogen peroxide;
In
methanol;
at -5 - 8 ℃;
for 5h;
Reagent/catalyst;
Temperature;
|
|
|
omeprazole sulfide;
With
titanium(IV) isopropylate; diethyl (2S,3S)-tartrate;
In
water; toluene;
at 45 ℃;
for 0.5h;
With
Cumene hydroperoxide; triethylamine;
In
water; toluene;
at 20 ℃;
for 4h;
Temperature;
Time;
|
-
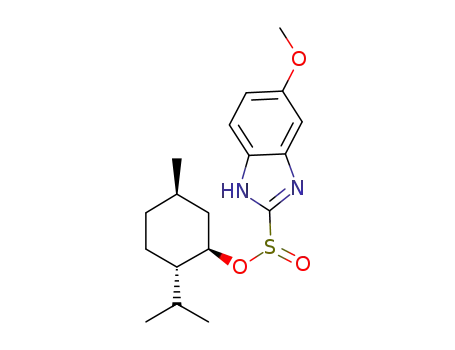
-
1080503-61-2
(-)-menthyl 5-methoxy-2-benzimidazolylsulphinate
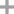
-
-
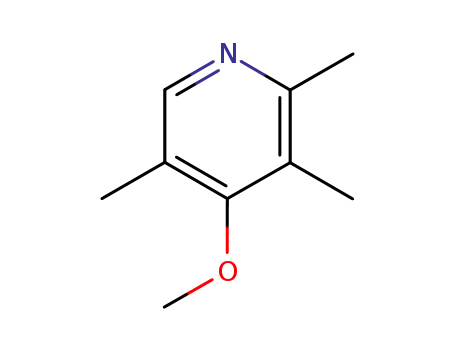
109371-19-9
4-methoxy-2,3,5-trimethylpyridine

-

-
73590-58-6
omeprazole
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
4-methoxy-2,3,5-trimethylpyridine;
With
n-butyllithium;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at -90 - -80 ℃;
for 0.5h;
(-)-menthyl 5-methoxy-2-benzimidazolylsulphinate;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at -80 - -20 ℃;
With
water;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at -20 ℃;
|
86% |
73590-58-6 Upstream products
-
73590-85-9

omeprazole sulfide
-
142885-92-5
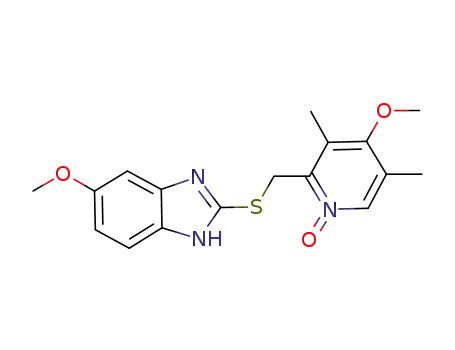
5-methoxy-2-[[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl-1-oxide)methyl]sulfanyl]-1H-benzimidazole
-
408332-88-7
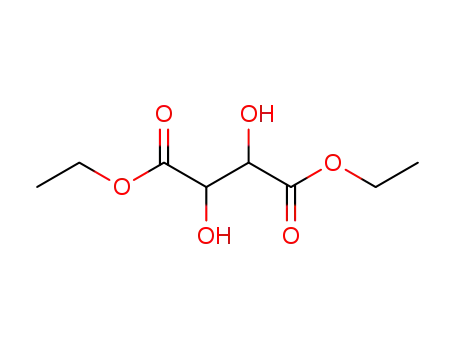
Diethyl tartrate
-
13811-71-7
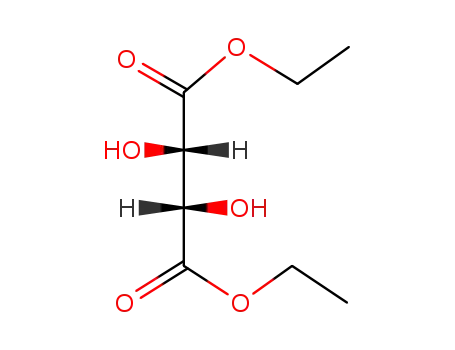
diethyl (2S,3S)-tartrate
73590-58-6 Downstream products
-
151602-49-2
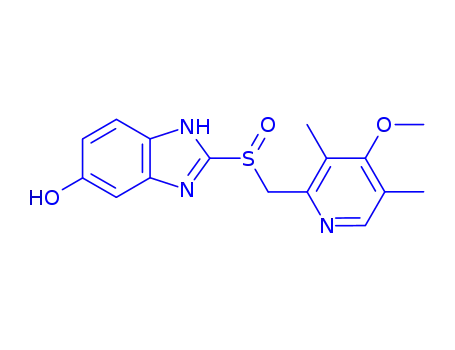
5-O-Desmethylomeprazole
-
651728-74-4
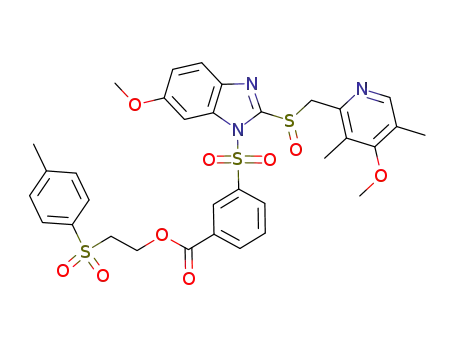
3-[6-methoxy-2-(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl-methanesulfinyl)benzimidazole-1-sulfonyl]benzoic acid 2-(toluene-4-sulfonyl)ethyl ester
-
651728-85-7
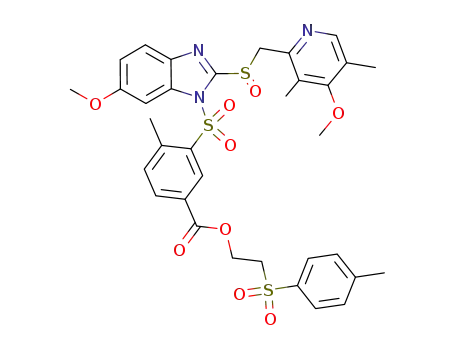
3-[6-methoxy-2-(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethyl-pyridin-2-ylmethanesulfinyl)-benzimidazole-1-sulfonyl]-4-methylbenzoic acid 2-(toluene-4-sulfonyl)ethyl ester
-
651729-03-2
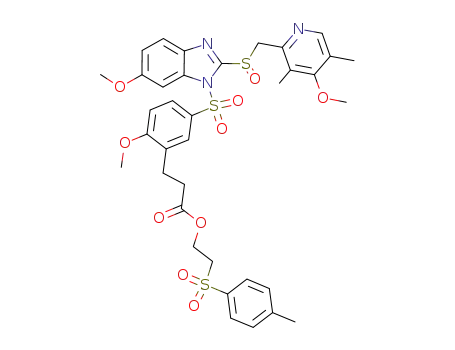
3-[2-methoxy-5-{6-methoxy-2-(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethyl-pyridin-2-ylmethanesulfinyl)-benzimidazole-1-sulfonyl}phenyl]propionic acid 2-[toluene-4-sulfonyl]ethyl ester
Relevant Products
-
Tesamorelin
CAS:218949-48-5
-
Chromium oxide
CAS:1308-38-9
-
5-Methyl-2-phenyl-1,2-dihydropyrazol-3-one
CAS:89-25-8