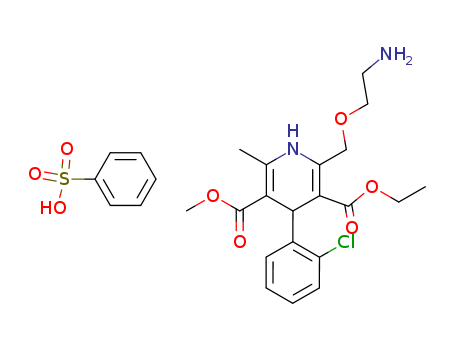
111470-99-6
- Product Name:Amlodipine besylate
- Molecular Formula:C20H25ClN2O5.C6H6O3S
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:567.06
Product Details;
CasNo: 111470-99-6
Molecular Formula: C20H25ClN2O5.C6H6O3S
Appearance: White powder
Manufacturer supply good quality Amlodipine besylate 111470-99-6 with stock
- Molecular Formula:C20H25ClN2O5.C6H6O3S
- Molecular Weight:567.06
- Appearance/Colour:White powder
- Vapor Pressure:3.34E-11mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:199-201 ºC
- Boiling Point:527.2 ºC at 760 mmHg
- PKA:8.6
- Flash Point:272.6 ºC
- PSA:162.63000
- Density:1.227 g/cm3
- LogP:5.30950
Amlodipine besylate(Cas 111470-99-6) Usage
|
Drug Classification and Use |
Amlodipine besylate belongs to the class of calcium channel blockers (CCBs) and is primarily used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). It is also utilized for the treatment of chronic stable angina and vasospastic angina. |
|
Pharmacokinetic Characteristics |
Amlodipine besylate is a dihydropyridine CCB with unique pharmacokinetic properties attributed to its high degree of ionization. The drug is available in both racemic and enantiomer forms, with the (鈭?)-(S)-enantiomer being primarily responsible for its pharmacological activity. |
|
Mechanism of Action |
Amlodipine besylate blocks the influx of calcium ions into cardiac and vascular muscles, leading to vasodilation and reduced blood pressure. |
|
Pharmaceutical Formulations |
Amlodipine besylate is formulated into various dosage forms for oral administration, including tablets. |
|
Solid Forms and Crystal Structures |
Amlodipine besylate exists in four solid forms: anhydrate, monohydrate, dihydrate, and amorphous. |
|
Dosage Equivalence |
Amlodipine besylate is often dosed in terms of its free base equivalent, with 6.9 mg equivalent to 5 mg of amlodipine free base. |
|
Manufacturing Techniques |
The direct compression process is used for manufacturing amlodipine besylate tablets due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional granulation technologies. |
|
Mechanism of action |
Amlodipine Besylate is a dihydropyridine calcium antagonist that prevents the transmembrane influx of calcium ions into the vascularsmooth and cardiacmuscle.It attaches to both dihydropyridine and non-dihydropyridine binding sites. The contractile manners of cardiac and vascular smooth muscle are dependent on the movement of extracellular calcium ions into these cells through specific ion channels. Amlodipine Besylate inhibits calcium ion influx across cell membranes selectively, with a superior effect on vascular smooth muscle cells than on cardiac muscle cells. |
|
side effects |
1. Heart Failure Calcium-channel blockers are normally avoided in patients with heart failure but ADB has not been found to have any adverse effects on morbidity or mortality in patients with severe heart failure. Therefore, it may be a suitable treatment option for angina pectoris or hypertension in such patients. However, a study on hypertensive patients found that ADB was less effective than the diuretic chlorthalidone in the prevention of heart failure. 2. Porphyria Although there have been reports of the successful use of ADB in patients with porphyria, some studies have reported the occurrence of acute exacerbation in such patients. 3. Miscellaneous Adverse Effects A number of other adverse events occurring in response to the regular use of ADB in 1091 patients with hypertension have been reported. Around 12% (128) patients stopped the intake of the drug due to the appearance of adverse effects. The most common reported adverse effects include ankle edema, flushing, headache, skin rash, and fatigue. |
|
Interaction with Combination Drugs |
The evaluation of pharmacokinetic interactions between Amlodipine Besylate(ADB), valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide revealed no clinically relevant interactions. Similarly, combination of ADB and olmesartan medoxomil is also known to have no impact on the pharmacokinetic profiles of individual drugs. Concomitant use of ADB and atorvastatin in patients with hypertension and dyslipidemia has shown to be well tolerated without any adverse pharmacodynamic interaction. The use of triple combination i.e. ADB + Olmesartan Medoxomil + hydrochlorothiazide has also demonstrated to be safe . |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: The benzenesulfonate salt of amlodipine. |
|
Manufacturing Process |
2-[(2-Aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-ethoxycarbonyl-5- methoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine (amlodipine) was prepared from 2-(phthalimidoaminoethoxy)acetoacetate, 2-chlorobenzaldehyde and methyl-3-aminocrotonate under refluxing in ethanol for 24 hours. The ketoester was prepared by the method of Troostwijk and Kellog (JCS Chem. Comm., 1977, p.932). Methyl-3-aminocrotonate can be prepared by known method. Phthalimido-amino-protecting group was removed using hydrazine hydrate in ethanol at the reflux temperature. Although amlodipine is effective as the free base, in practice it is best administered form of a salt of a pharmaceutically acceptable acid. Benzensulphonic salt of amlodipine was prepared as follows: Amlodipine base (65.6 g, 0.161 mols) was slurried in industrial methylated spirit (denatured alcohol, 326.4 ml) and cooled to 5°C. Benzensulphonic acid (26.2 g, 0.168 mols) was dissolved in industrial methylated spirit (65.6 ml) at 5°C and added to base. The resulting slurry was then granulated, filtered and washed with 2 volumes the same solvent (65.6 ml). The damp solid was slurred at 5°C for 1 hr in 327.6 ml industrial methylated spirit, filtered, washed with 2 volumes of the same solvent (65.6 ml) and dried under vacuum at 55°C for 24 hr. A yield of besylate salt of amlodipine 65 g. |
|
Brand name |
Norvasc (Pfizer);Istin. |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Antianginal, Antihypertensive |
|
General Description |
Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control, provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards. Amlodipine besylate is a calcium channel blocker, which inhibits the trans membrane influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscles and cardiac muscle. It belongs to the dihydropyridine family. It is used in combination with atorvastatin calcium to treat vasospastic angina, chronic stable angina, hypertension, in elevated serum triglyceride levels, primary dysbetalipoproteinemia. |
|
Biological Activity |
L-type calcium channel blocker that displays antihypertensive properties. Inhibits Ca 2+ -induced contractions in depolarized rat aorta (IC 50 = 1.9 nM) and displays vasoprotective effects in cardiovascular disease. Inhibits proliferation of human vascular smooth muscle cells and epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells (IC 50 = 25 μ M). |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Amlodipine is an L-type calcium channel blocker. Amlodipine belongs to a class of cardiovascular drugs, which act at the voltage gated calcium channel of the CaV1, or L-type, class. Amlodipine also has antihypertensive and antianginal effects. Its activity resides mainly in the (-)-isomer. Amlodipine inhibits growth of human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells and has antireproductive effects in male rats. |
|
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments |
Oral amlodipine appears to be a useful agent in the treatment of hypertension in cats and many consider it the drug of choice for this indication. In pharmacokinetic studies, amlodipine has decreased blood pressure in dogs with chronic renal disease, but its efficacy in treating hypertensive dogs has been disappointing. Hypertension in cats is usually secondary to other diseases (often renal failure or cardiac causes such as thyrotoxic cardiomyopathy or primary hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, etc.) and is most often seen in middle-aged or geriatric cats. These animals often present with acute clinical signs such as blindness, seizures, collapse or paresis. A cat is generally considered hypertensive if systolic blood pressure is >160 mmHg. Early reports indicate that if antihypertensive therapy is begun acutely, some vision may be restored in about 50% of cases of blindness secondary to hypertension. |
|
references |
[1] lee yj, park hh, koh sh, choi ny, lee ky. amlodipine besylate and amlodipine camsylate prevent cortical neuronal cell death induced by oxidative stress. j neurochem. 2011 dec;119(6):1262-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07529.x. [2] yoshida j, ishibashi t, nishio m. antiproliferative effect of ca2+ channel blockers on human epidermoid carcinoma a431 cells. eur j pharmacol. 2003 jul 4;472(1-2):23-31. [3] henik ra, snyder ps, volk lm. treatment of systemic hypertension in cats with amlodipine besylate. j am anim hosp assoc. 1997 may-jun;33(3):226-34. |
InChI:InChI=1/C20H25ClN2O5.CH4O3S/c1-4-28-20(25)18-15(11-27-10-9-22)23-12(2)16(19(24)26-3)17(18)13-7-5-6-8-14(13)21;1-5(2,3)4/h5-8,17,23H,4,9-11,22H2,1-3H3;1H3,(H,2,3,4)
111470-99-6 Relevant articles
A pharmaceutical model intermediate and its preparation method
-
Paragraph 0038; 0047; 0053-0055; 0058, (2019/01/22)
The invention relates to a novel interme...
Synthesis process of amlodipine besylate
-
Paragraph 0006; 0014; 0015; 0027-0030, (2018/09/14)
The invention discloses a synthesis proc...
Method for preparing amlodipine besylate tablet by one-pot method
-
Paragraph 0014, (2018/09/21)
The invention relates to a method for pr...
Using the new crystal form [...] and production of high-purity [...]
-
Paragraph 0016; 0069; 0070; 0074, (2017/02/17)
PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED: To provide a proce...
111470-99-6 Process route
-
![4-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-ethoxycarbonyl-5-methoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-2-[2-phthalimidoethoxymethyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine](/upload/2025/4/f111f03b-fb20-4d71-b103-080ef149c250.png)
-
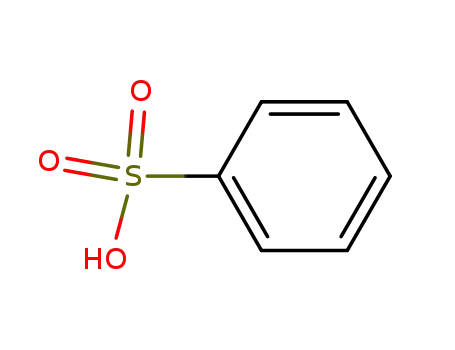
88150-62-3,103094-30-0
4-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-ethoxycarbonyl-5-methoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-2-[2-phthalimidoethoxymethyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine
-
-
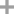
98-11-3
benzenesulfonic acid

-
-
111470-99-6
amlodipine besylate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
4-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-ethoxycarbonyl-5-methoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-2-[2-phthalimidoethoxymethyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine;
With
methylamine;
at 25 ℃;
Large scale;
benzenesulfonic acid;
In
water;
at 30 ℃;
Temperature;
Large scale;
|
91.6% |
|
4-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-ethoxycarbonyl-5-methoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-2-[2-phthalimidoethoxymethyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine;
With
methylamine;
In
water;
at 20 - 45 ℃;
for 4.5h;
benzenesulfonic acid;
In
water;
at 20 ℃;
for 4.5h;
pH=1 - 2;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
|
|
4-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-ethoxycarbonyl-5-methoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-2-[2-phthalimidoethoxymethyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine;
With
hydrazine;
In
methanol; ethyl acetate;
at 34 - 37 ℃;
for 0.05h;
Inert atmosphere;
benzenesulfonic acid;
In
isopropyl alcohol;
at 5 - 30 ℃;
for 2h;
|
|
|
4-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-ethoxycarbonyl-5-methoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-2-[2-phthalimidoethoxymethyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine;
With
methylamine;
In
dichloromethane;
at 25 ℃;
for 4h;
benzenesulfonic acid;
In
dichloromethane;
at 25 ℃;
|
48 g |
-
![2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-ethoxycarbonyl-5-methoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine](/upload/2025/4/de9ea361-92e5-497e-8924-baedc7ec3a1b.png)
-
88150-42-9
2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-ethoxycarbonyl-5-methoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine

-

-
98-11-3
benzenesulfonic acid

-

-
111470-99-6
amlodipine besylate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In
methanol; toluene;
at 0 - 20 ℃;
for 2h;
|
87% |
|
for 3h;
|
|
|
In
isopropyl alcohol;
at 0 - 30 ℃;
for 2 - 2.25h;
Product distribution / selectivity;
|
|
|
In
methanol;
at 50 ℃;
|
|
|
2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-ethoxycarbonyl-5-methoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine;
pyrographite;
In
isopropyl alcohol;
at 55 - 60 ℃;
for 0.5h;
benzenesulfonic acid;
In
isopropyl alcohol;
at 25 - 50 ℃;
for 3.5h;
|
|
|
In
isopropyl alcohol;
at 27 - 43 ℃;
for 1h;
|
111470-99-6 Upstream products
-
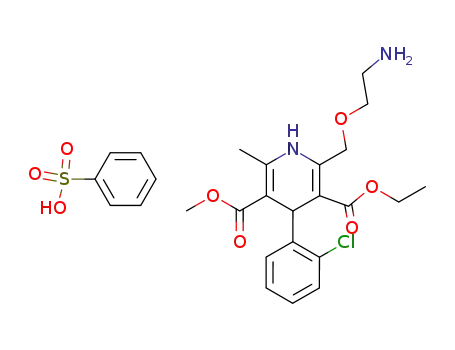
156366-27-7
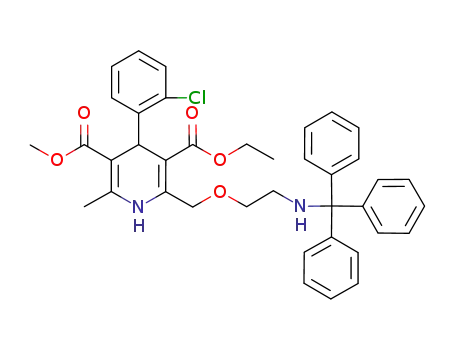
N-tritylamlodipine
-
98-11-3

benzenesulfonic acid
-
88150-42-9
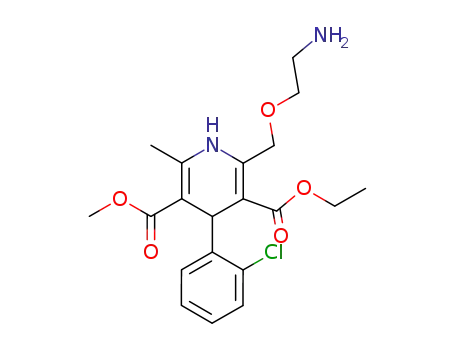
2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-ethoxycarbonyl-5-methoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine
-
246852-12-0
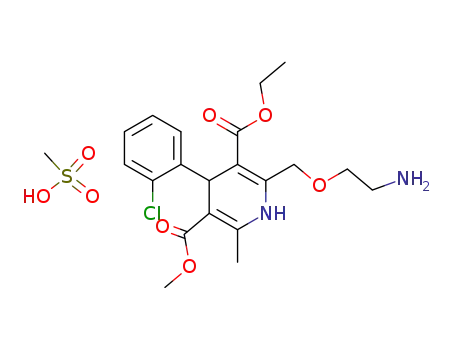
amlodipine mesylate
111470-99-6 Downstream products
-
852990-75-1
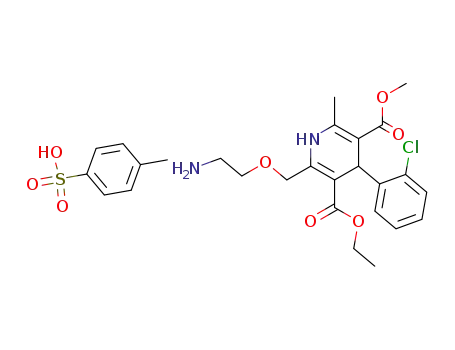
amlodipine p-toluene sulfonate
-
150566-71-5
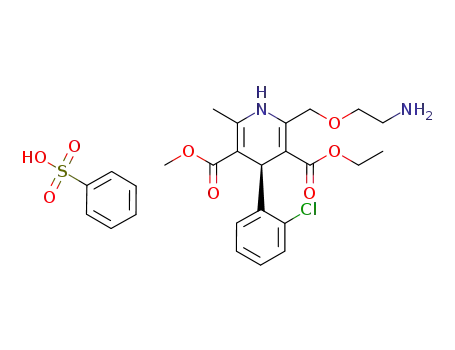
(-)-Amlodipine besylate
-
828247-64-9
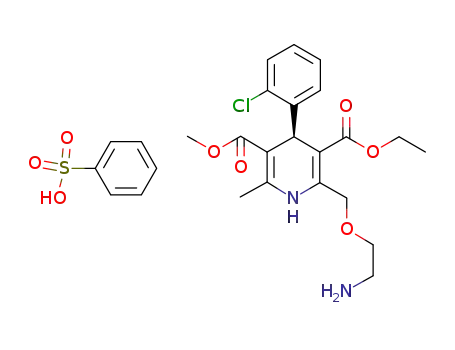
(+)-Amlodipine besylate
Relevant Products
-
D-Glucosamine hydrochloride
CAS:66-84-2
-
hyaluronic acid
CAS:9004-61-9
-
SLU-PP-332
CAS:303760-60-3